Ductal Carcinoma in Situ (DCIS)
What is ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS)?
DCIS (ductal carcinoma in situ) is a non-invasive breast cancer. It’s stage 0 breast cancer.
With DCIS, the abnormal cells are contained in the milk ducts and have not invaded nearby tissue outside the milk ducts. (The milk ducts are canals that carry milk from the lobules to the nipple openings during breastfeeding.)
It’s called “in situ” (which means “in place”) and “non-invasive” because the abnormal cells have not left the milk ducts.
DCIS is also called intraductal (within the milk ducts) carcinoma. Some people use the terms “pre-invasive” or “pre-cancerous” to describe DCIS.
Both women and men can get DCIS.
DCIS is treated to try to prevent the development of invasive breast cancer.
Learn about treatment for DCIS.
Learn more about breast cancer stages and staging.
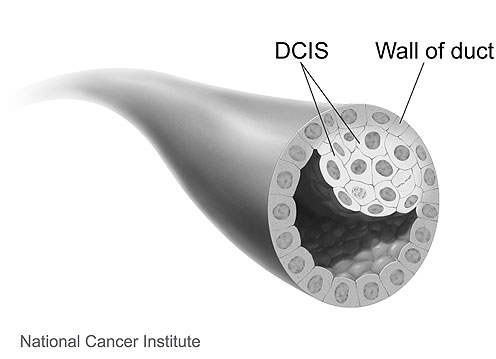 |
Image source: National Cancer Institute (www.cancer.gov) |
The following is a 3D interactive model showing DCIS. The labels show a normal duct and a duct with DCIS.
DCIS diagnosed with invasive breast cancer
DCIS can be found alone or with invasive breast cancer.
If it’s diagnosed with invasive breast cancer, treatment and the chances of survival are based on the invasive breast cancer, not the DCIS.
Learn about treatment for early breast cancer.
Treatment and survival for DCIS
Surgery is recommended as the first step to treat DCIS. After surgery, some people will have radiation therapy, and some may take hormone therapy.
With treatment, the chances of survival for DCIS are usually excellent.
Learn more about treatment for DCIS.

Kornelia Polyak, M.D., Ph.D.
Komen Scientific Advisory Board member
“Understanding why some patients with DCIS develop invasive breast cancer, while others do not, would help identify the drivers of tumor progression and the design of more effective therapies.”
Why is DCIS treated?
DCIS is non-invasive, but without treatment, the abnormal cells could progress to invasive cancer over time.
Health care providers cannot predict which cases of DCIS will progress to invasive breast cancer and which will not. Because DCIS might progress to invasive breast cancer, almost all cases of DCIS are treated.
Risk of developing invasive breast cancer after DCIS
After treatment for DCIS, there’s a small risk of:
- DCIS recurrence (a return of DCIS)
- Invasive breast cancer
These risks are higher with a lumpectomy plus radiation therapy than with a mastectomy [233]. However, overall survival is the same after either treatment [233].
Higher grade DCIS appears more likely than lower grade DCIS to progress to invasive breast cancer after treatment (surgery, with or without radiation therapy) [6].
With close follow-up, invasive breast cancer is usually caught early and can be treated effectively.
Learn about treatment for DCIS.
Updated 03/28/25
This content is regularly reviewed by an expert panel including researchers, practicing clinicians and patient advocates.



